1. Definition
It is the union of two universal joints through a telescopic shaft (tube/bar, tube/tube, and telescopic shafts). The cardan is the most widespread and efficient means of transmitting torque and rotation between a motor source (tractor) and an agricultural implement, whether it is a drag, 3-point coupling, or stationary implement.
The good performance and durability of the cardan shaft depend on:
- performing periodic maintenance according to the instructions in the manual.
- its correct application, that is, to determine the cardan type and size suitable for the work to be performed.
- the quality of its components concerning material and manufacture.
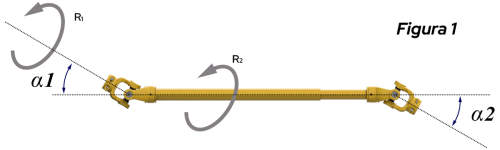
Once the requirements above are met, the useful life of the cardan shaft becomes directly proportional to the articulation angle α1 and α2, to which the terminals are subjected during work.
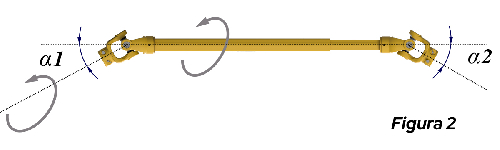
In the case of Figures 1 and 2, where the angles are the same, there is a tendency to compensate for the irregularity of the rotational movement (R1 and R2). In this case, the occurrence of irregularities is minimal and does not affect the cardan's durability.
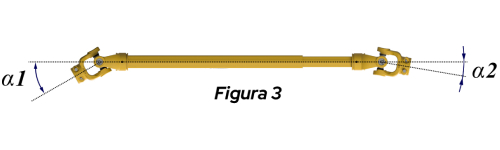
For Figure 3, where the angles are different, the greater the difference between them, the greater the irregularity of the rotational movement. This irregularity generates noise and vibrations that will shorten the useful life of your components.
2. Correct use of agricultural cardans
Other factors that influence the durability of cardans are torque peaks and the variations that occur during work due to the sand bank, soil irregularity, excess power, PTO activation, and other types of situations that occur during fieldwork. There are safety devices for that.
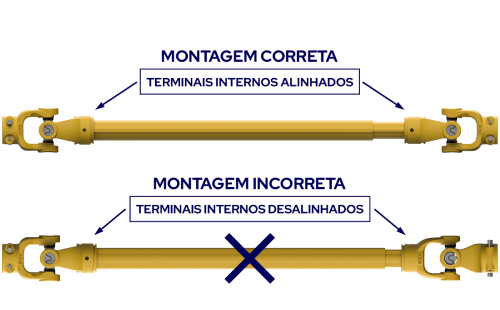
Special attention must be given to the assembly of the tube and bar in the square profile cardans. The internal terminals must be aligned as shown in the figure beside. Misaligned terminals generate vibrations, wear, breakage, and excessive heating of the crossheads.
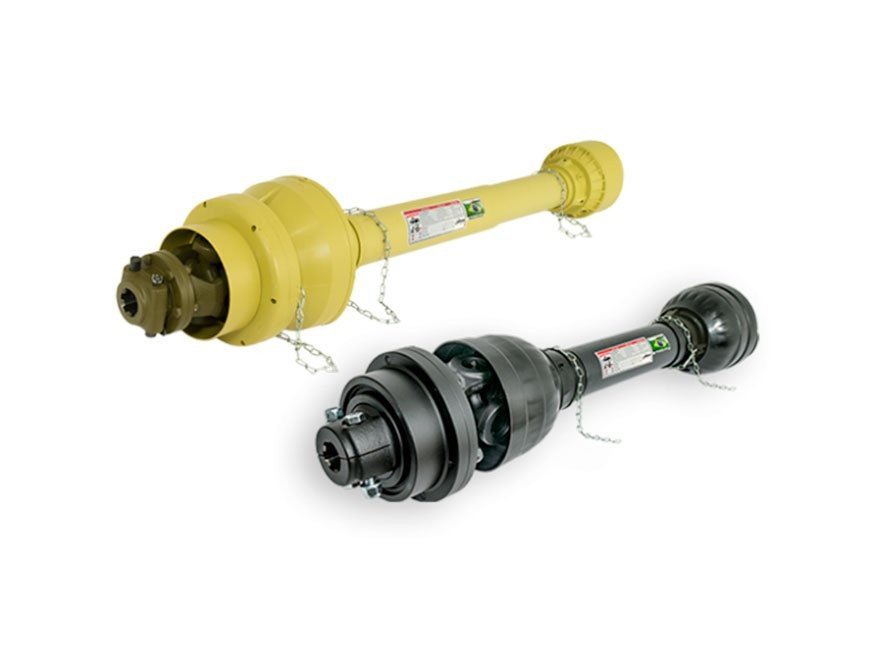
3. Composition of cardans
Conventional square cardan without safety devices.
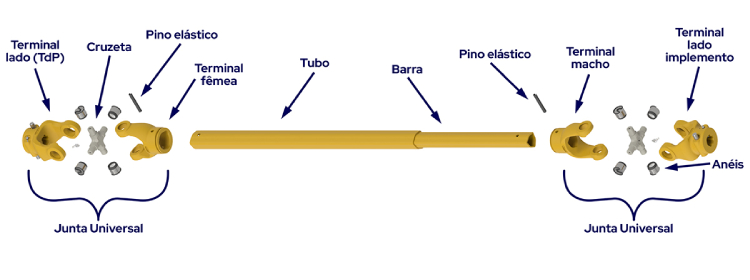
The oval and triangular cardans have the same components, only the tube profiles change.
4. Classification of the cardans
Agricultural cardans, in general, are developed in compliance with regulatory standards. Therefore, cardan components are interchangeable within the same series, even between different brands.
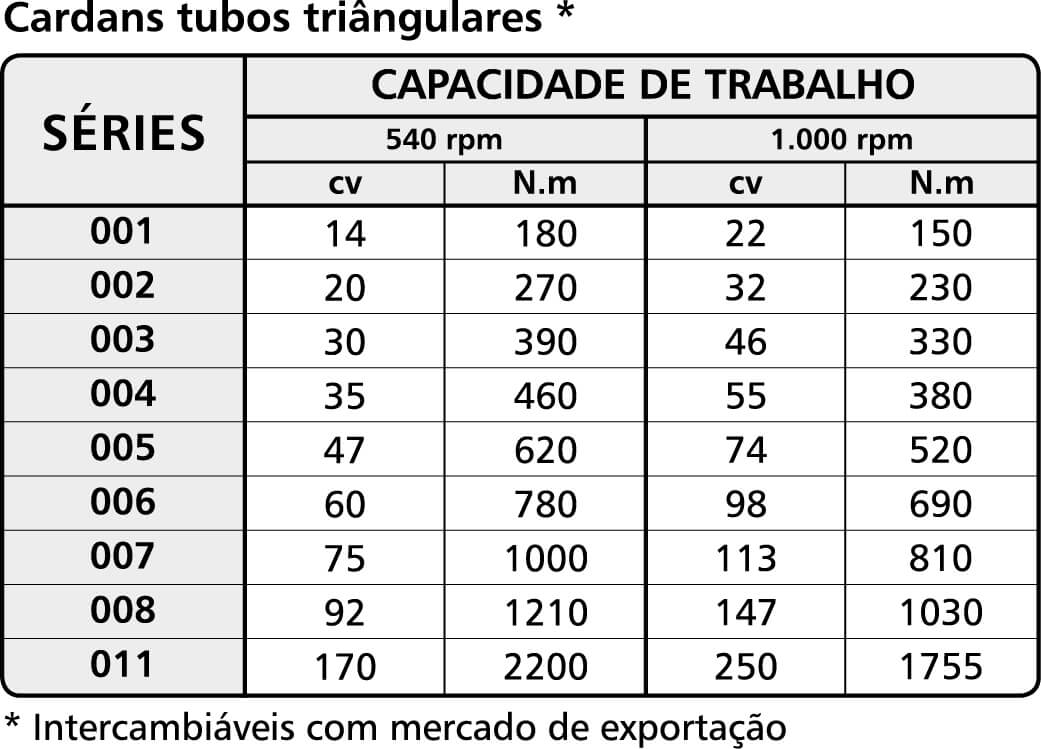
Each manufacturer has its classification. AEMCO classifies it into “Series” and each series has its application or torque capacity.
The following tables indicate the power (in cv) and torque (in N.m) in the normal working regime for which each series is indicated.
Table 1: Square tube cardans.
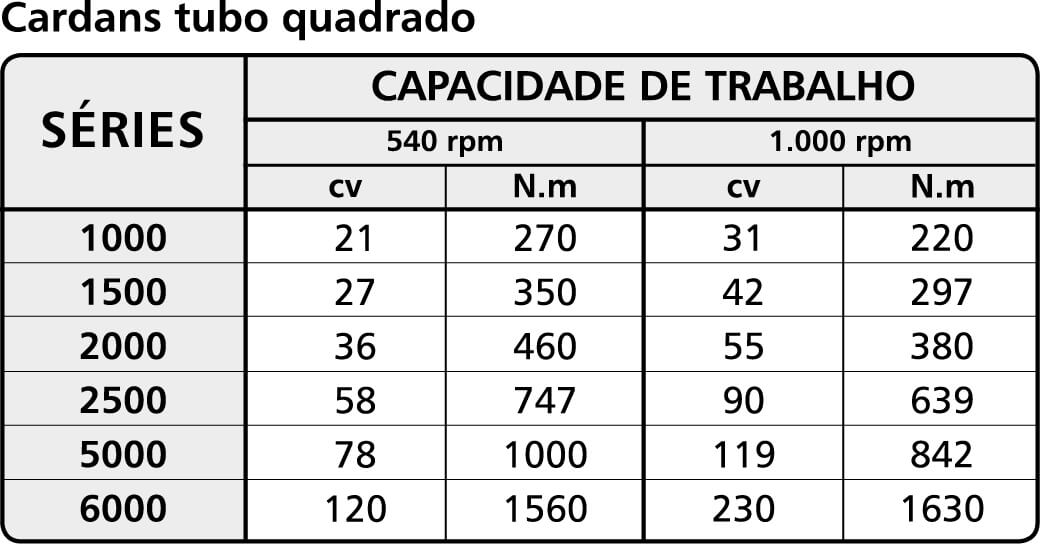
Table 2: Oval tube cardans
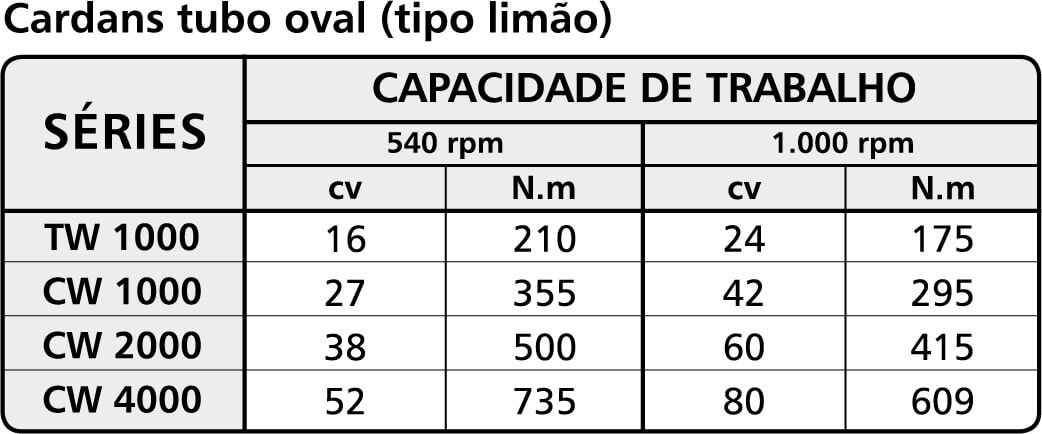
Table 3: Triangular homokinetic tube Cardans
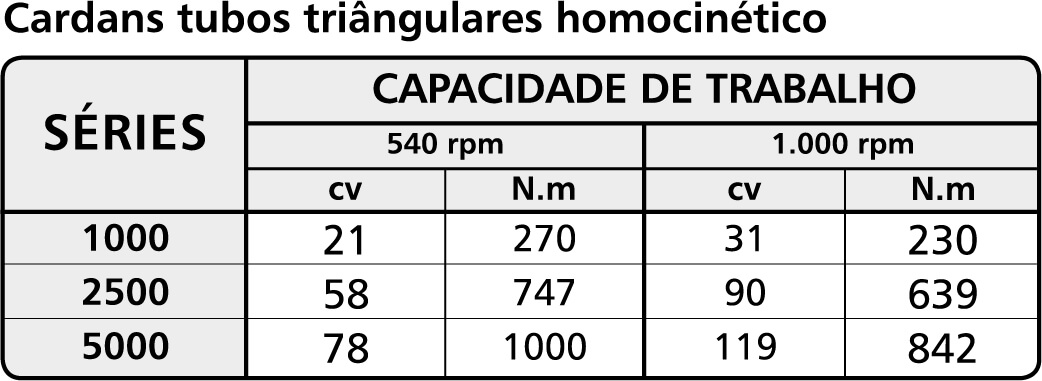
Table 4: Triangular tube cardans
5. Conventional and Homokinetic Cardans
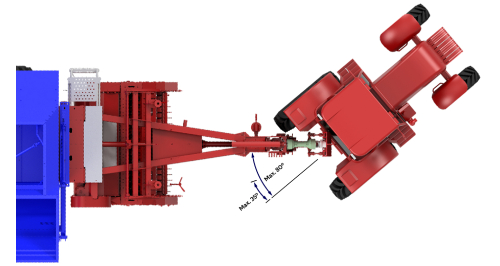
Conventional: these cardans have limitations regarding the maximum angle of articulation. This angle, with the cardan in operation, can reach a maximum of 35° (picture at the side), for a short period. In continuous work, it must not exceed 15°.
Homokinetic: in this case, due to a central body that joins two terminals, the working angle can reach 80° for a short period, facilitating certain types of operation, such as headland maneuvers. In continuous work, this angle must be a maximum of 16° for 540 rpm and 9° for 1000 rpm.

Note: Some operational care must be taken when using homokinetic cardans:
- Never activate the PTO when the joint is at an angle greater than 16° at 540 rpm and 9° at 1000 rpm.
- When maneuvering with the PTO turned off, never exceed a 50° articulation angle. This can occur during transport routes or maneuvers in sheds with the cardan attached.
- Never go in reverse with the homokinetic cardan off. For questions, consult the cardan manufacturer.